On Curvenote, blocks are distinct sections of content. In Jupyter, cells are the distinct sections of content that make up a notebook. When notebooks are saved on Curvenote the cells from Jupyter are considered blocks. While there are different types of cells in Jupyter, each cell is version individually and can be reused throughout your content on Curvenote. You can interact with blocks/cells on either Curvenote or Jupyter (using the Curvenote Jupyter Extension). Learn how to edit, run, save and version blocks/cells below, and how to reuse your blocks/cells in Reusing Blocks.
Cell Types¶
There are three types of cells that can exist in notebook from Jupyter. The type of cell is passed between Jupyter and Curvenote as certain restrictions and connections exist depending on the cell type.
Code Cells¶
Code cells typically contain lines of code and/or comments that can be run in Jupyter. Code cells can produce an associated Output cell that contain text, a static image, a table, or an interactive plot. Currently Curvenote does not run code, as such Code cells can only be viewed on Curvenote, and only be edited and run in Jupyter.
Output Cells¶
Output cells are created when a Code cell is run and can contain text, a static image, a table, or an interactive plot. Output cells are automatically linked to their associated Code cell, but are versioned individually and independently of their Code cell (their version numbers may not match). Output cells can only be changed when their Code cells are run in Jupyter, as such they can only be viewed on Curvenote.
Markdown Cells¶
Markdown cells contain rich text features and formatting including HTLM and math. These cells are the most similar to a Curvenote block, which can also use such rich text formatting. Markdown cells can be edited in both Jupyter and Curvenote, and any block added to a notebook, then opened in Jupyter is considered a Markdown cell.
Curvenote Jupyter Extension¶
The Curvenote Jupyter extension for Google Chrome allows you to access Curvenote features directly while working with your notebook in either Jupyter Lab or Notebook. Learn more ➡️ Curvenote Jupyter Extension Cells within a notebook can be edited and run as they normally would in Jupyter, then saved and versioned with Curvenote.
Save Cell Version¶
All cells are versioned individually, but a new version of a cell is only created and saved when that cell has changes since the last save, and the entire notebook is saved. Learn more about saving versions of your notebook and the cells within it Versioning Notebooks.
Change Status Icons¶
The cell version number is displayed on the far right of the cell in Jupyter. The status of changes within that cell are indicated by the change status icon located to the left of the cell version number. The following status options are possible:

- The cell the latest saved version and there are no changes since the notebook has been saved.
- Changes exist in the cell since the last saved version. If you hover over the icon the type of change(s) is specified as content/code, outputs, or local outputs, depending on the type of cell.
- Newer saved versions of the cell exist, but currently the cell displayed is Version 3, without any changes from when that version was saved.
- Newer saved versions of the cell exist, but currently the cell displayed is Version 2 with changes. If you hover over the icon the type of change(s) is specified as content/code, outputs, or local outputs, depending on the type of cell.
Compare and Use Versions¶
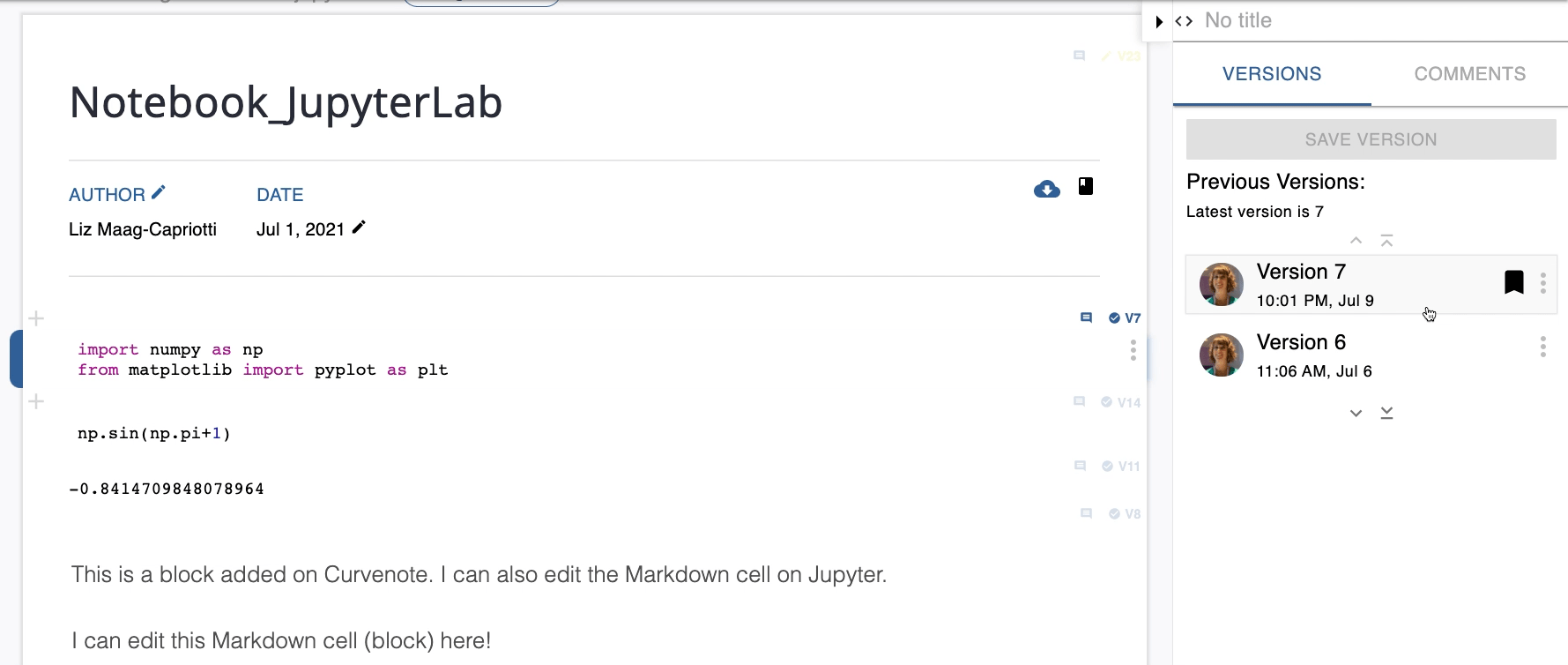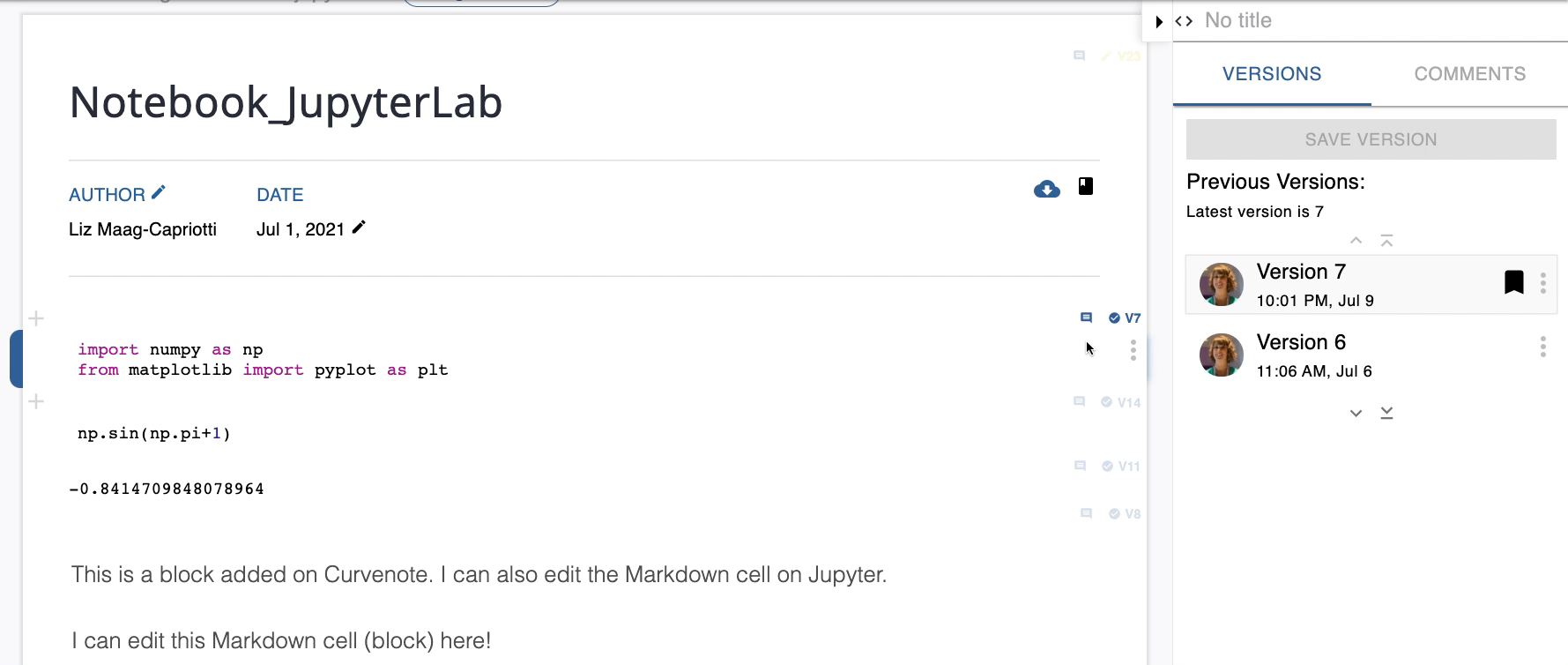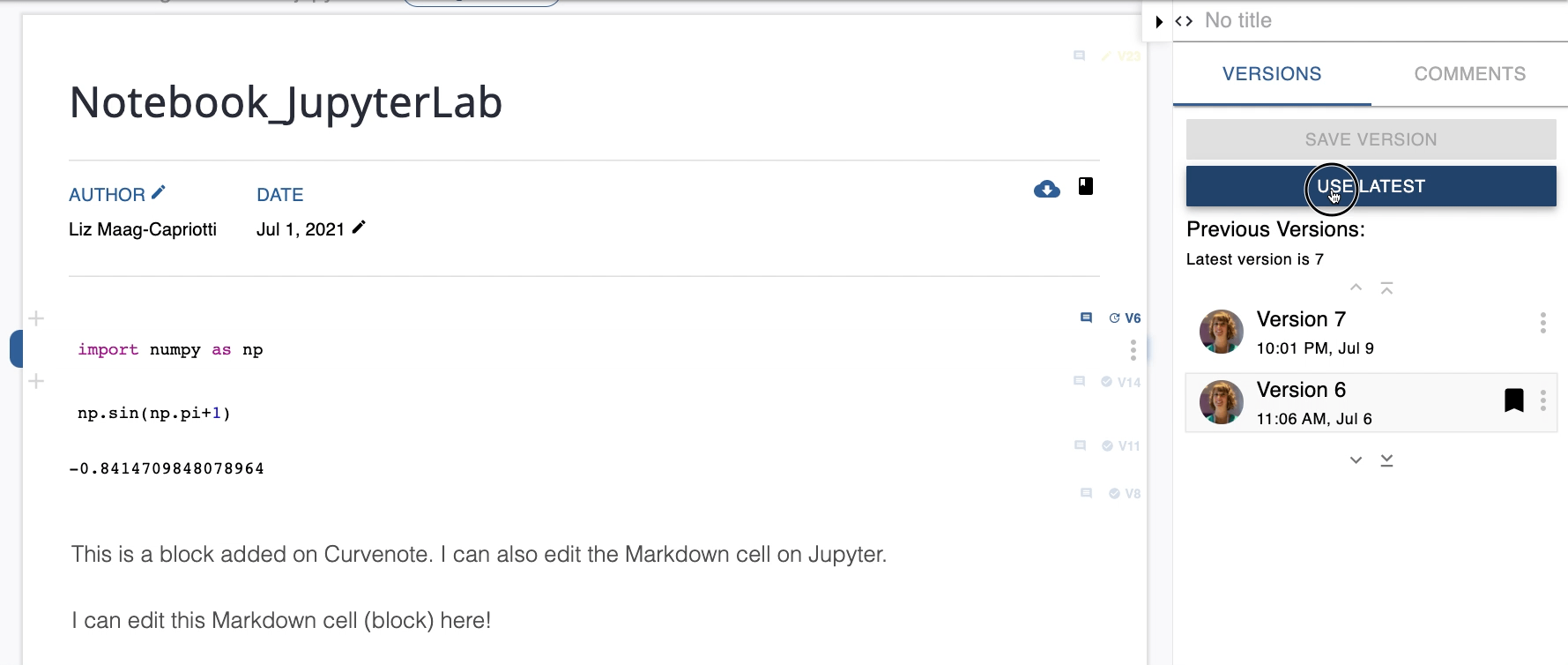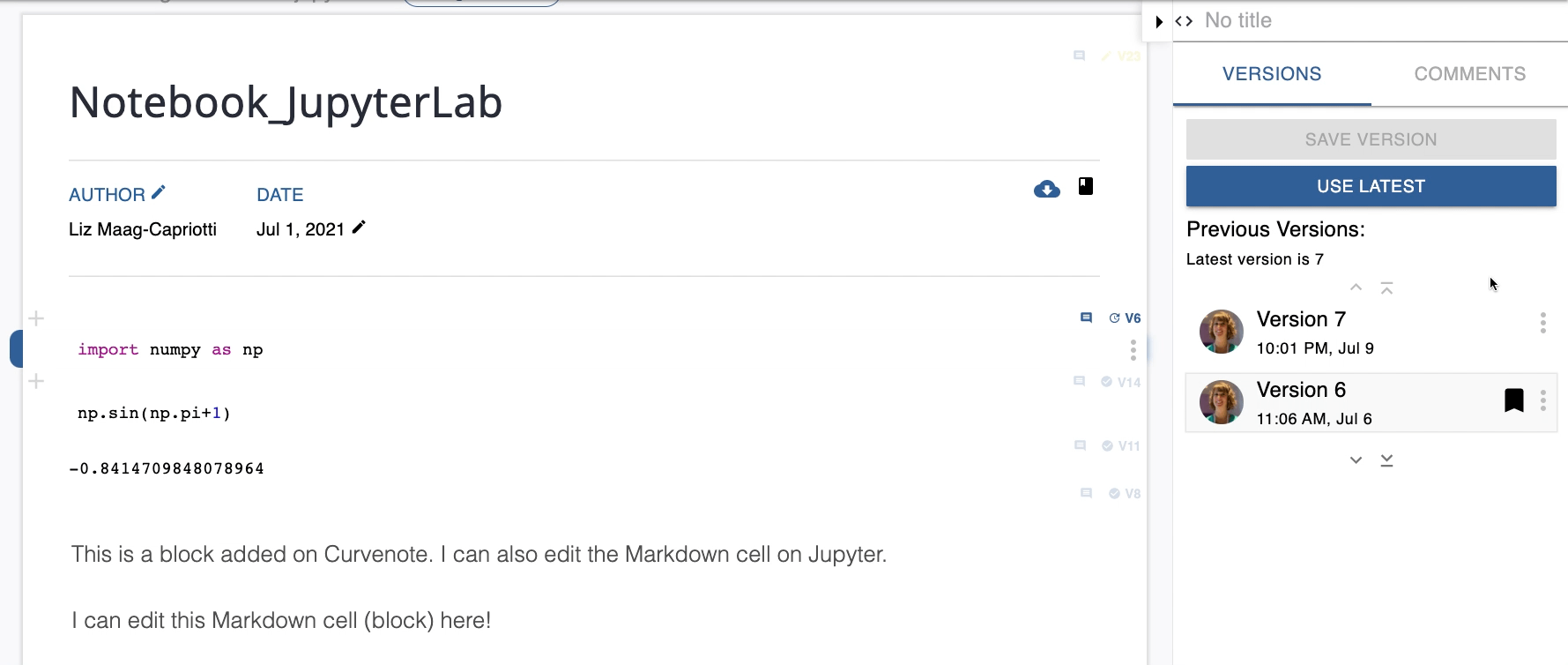
You can compare and switch between different versions of your cell. The Curvenote Jupyter extension panel lists all previous versions of your cell in the Selected Cell section by number, and displays the time and date that they were saved. The current version is indicated by the bookmark icon. Comparisons can be made between saved versions of a cell and/or the current version of a cell with changes.
To compare and/or switch between two versions of a cell:
- Select the cell.
- Expand the Curvenote Jupyter extension panel.
- Expand the Selected Cell section.
- Select the Version # you want to compare to the current version.
- A side-by-side comparison window will appear below the selected cell.
- The differences between the two versions are highlighted.
- You can make changes to the current version of the cell (right panel).
- To add these changes to the current version, click UPDATE CELL.
- If you wish to use the selected Version # (left panel) either:
- Click USE VERSION # at the bottom of the comparison.
- Open the Options menu for the version in the extension panel.
- Select Use Version.
The version you have selected to use will now appear in place of the cell. If that cell had an associated output, that output will also be visible. Output versions cannot be viewed and compared in Jupyter.
Curvenote¶
Cells in Jupyter are blocks in Curvenote. When you access your notebook on Curvenote, you can enter draft mode to edit and save new versions of Markdown cells. You can also add blocks that will be considered Markdown cells when you open your notebook in Jupyter. On Curvenote you can view and use different versions of any type of cell and update the block settings.
Add, Edit, Save Markdown Blocks¶
To make changes to your notebook on Curvenote, you must be in Draft Mode. If you are not in Draft Mode, click EDIT in the app bar at the top of the page.
To add/import a block (Markdown cell) to your notebook:
- Select the block you want to add a block above or below.
- To add a new block, click the corresponding ➕ to where you want to add a new block (above or below).
- To import a block, open the More Options menu to the right of the ➕.
- Select Import Block.
- Paste the oxa link to the block you want to import. Learn more about importing and reusing blocks/cells Reusing Blocks.
- Make the desired changes.
- For these changes to be available in Jupyter, save a new version of the notebook by clicking SAVE VERSION in the app bar at the top of the page.
To edit a block (Markdown cell) in your notebook:
- Open a draft of the block via one of the following:
- Double click on the block
- Select the cell and hit ENTER.
- Open the block Options menu and select Edit.
- Make the desired changes.
- For the changes to be available in Jupyter, you can either save a version of the block or the notebook.
- To save only a version of the cell:
- Click SAVE VERSION in the block details panel.
- Open the block Options menu and select Save Version.
- To save a version of the notebook:
- Click SAVE VERSION in the app bar at the top of the page.
- To save only a version of the cell:
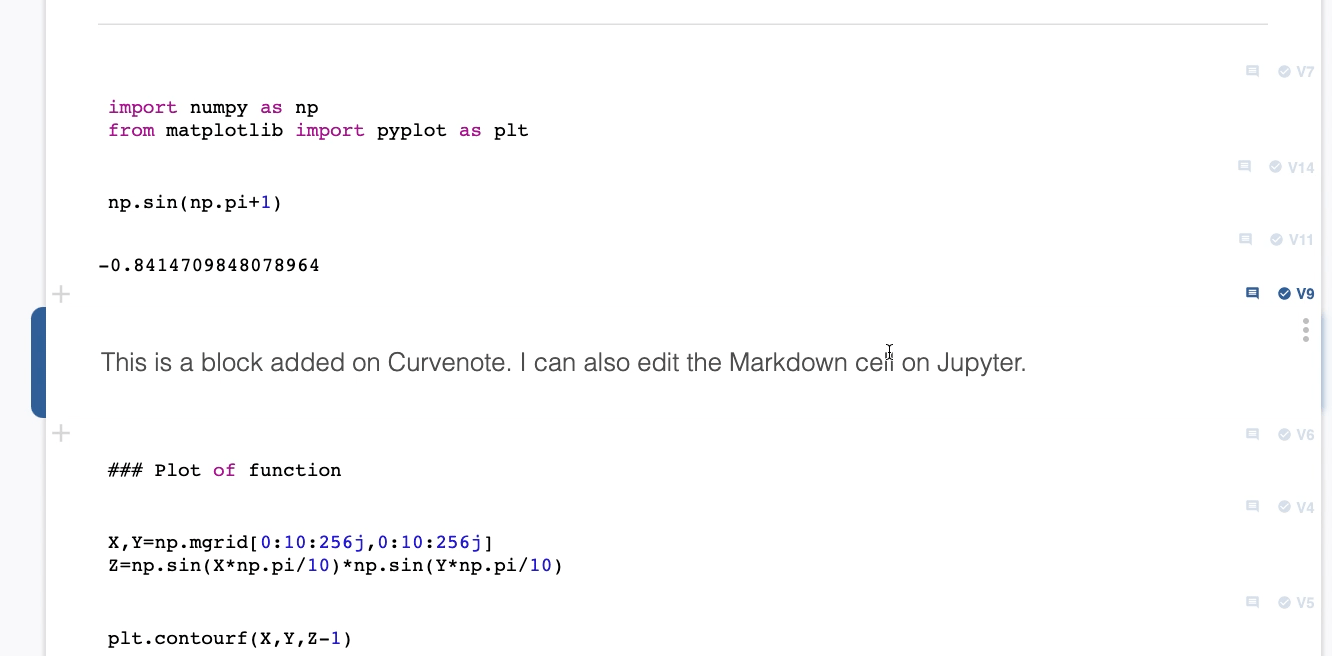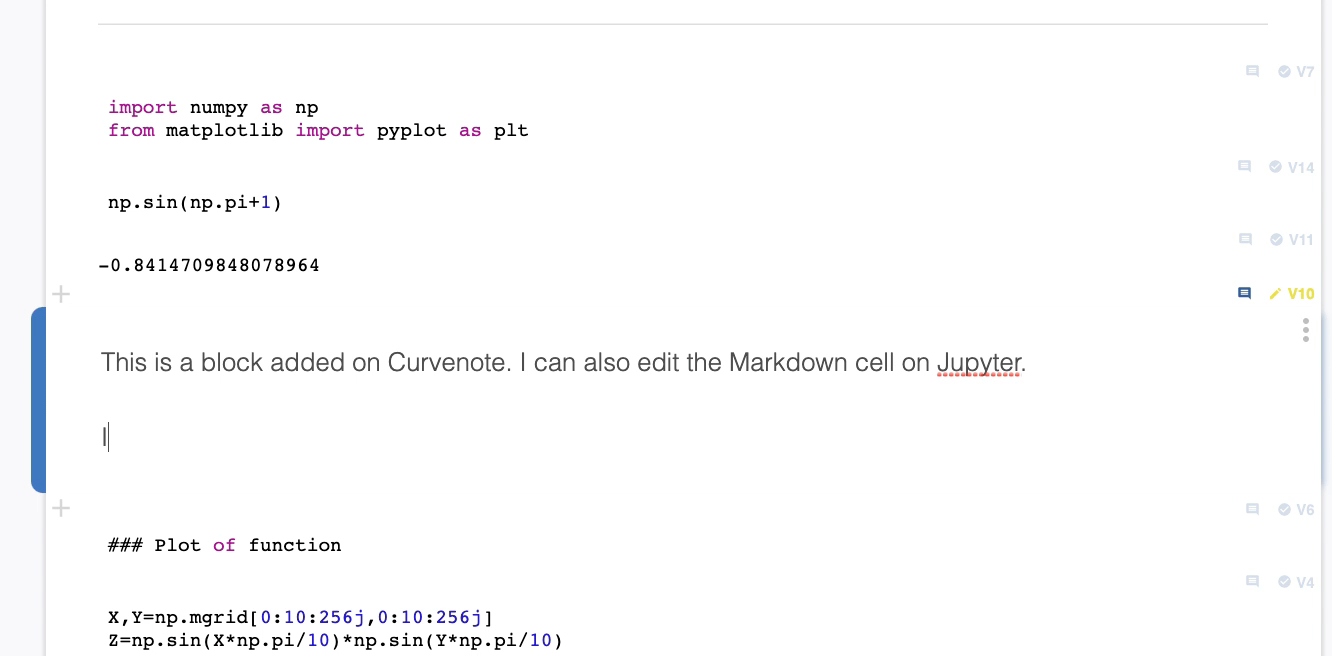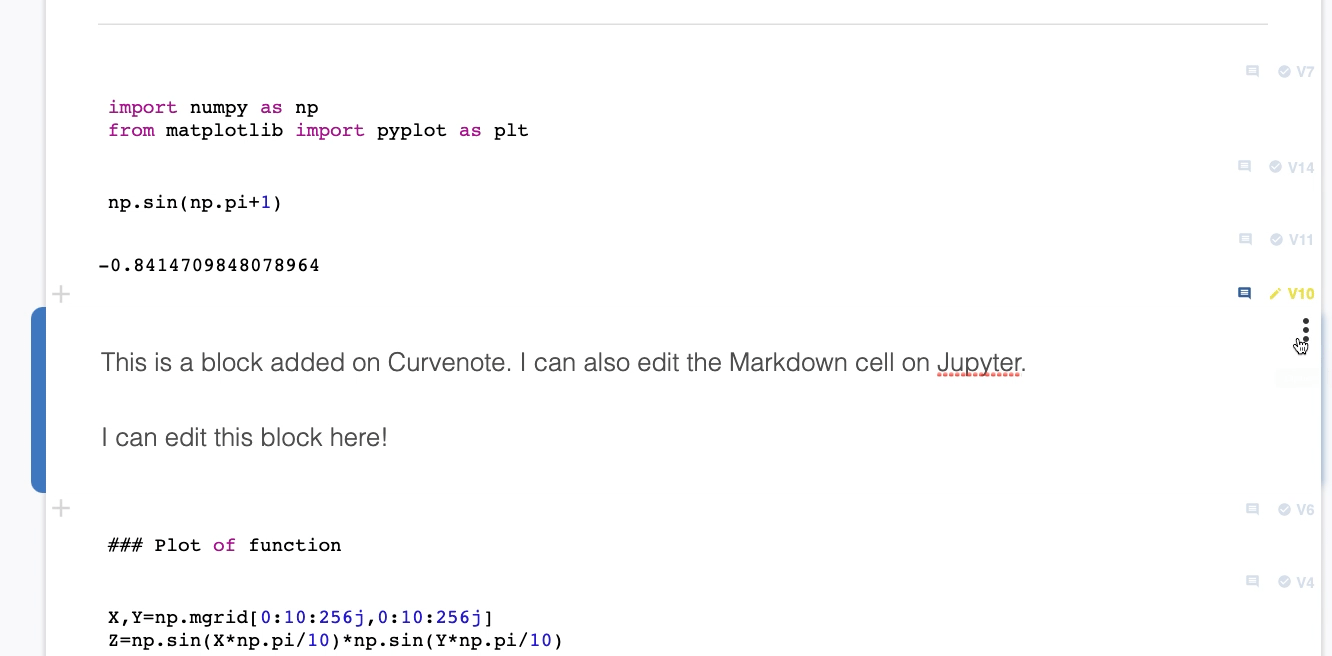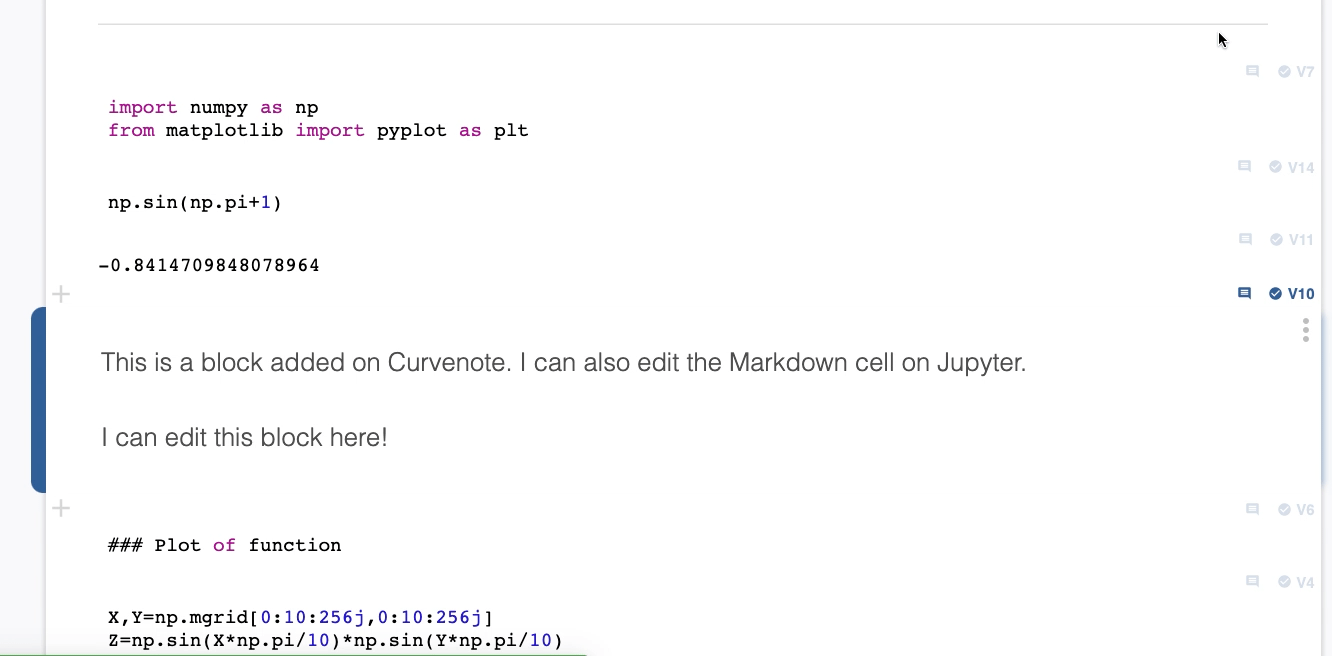
Preview and Use Previous Versions¶
You can preview and switch between different versions of a block/cell on Curvenote, not matter the type of cell. To preview and/or use a different version:
- Select a block.
- Expand the Block Details Panel.
- Select a Version #.
- This version will appear in place of the current version of the block as a preview.
- If you do not want to switch versions:
- Click CLEAR PREVIEW either on the block or in the Block Details Panel.
- If you want to switch to the selected version, either:
- Click the USE VERSION # button at the top of the Block Details Panel
- Open the version Options menu and select Use Version.
Block Settings¶
Blocks can viewed, edited, and reused on their own. In some instances it’s beneficial to include additional information with a block. The block settings allow you to add or update the URL, tag, and thumbnail. To update the block settings:
- Open the block Options menu below the version number.
- Select ⚙️ Block Settings.
- Update the URL and tags.
- To add a tag, hit ENTER after you are finished add the tag text. To remove the tag, click the to the right of the text.
- Click UPDATE SETTINGS.
- Drag and drop or click Browse to add an image from your computer.
Adjust your image.
Click UPLOAD.